a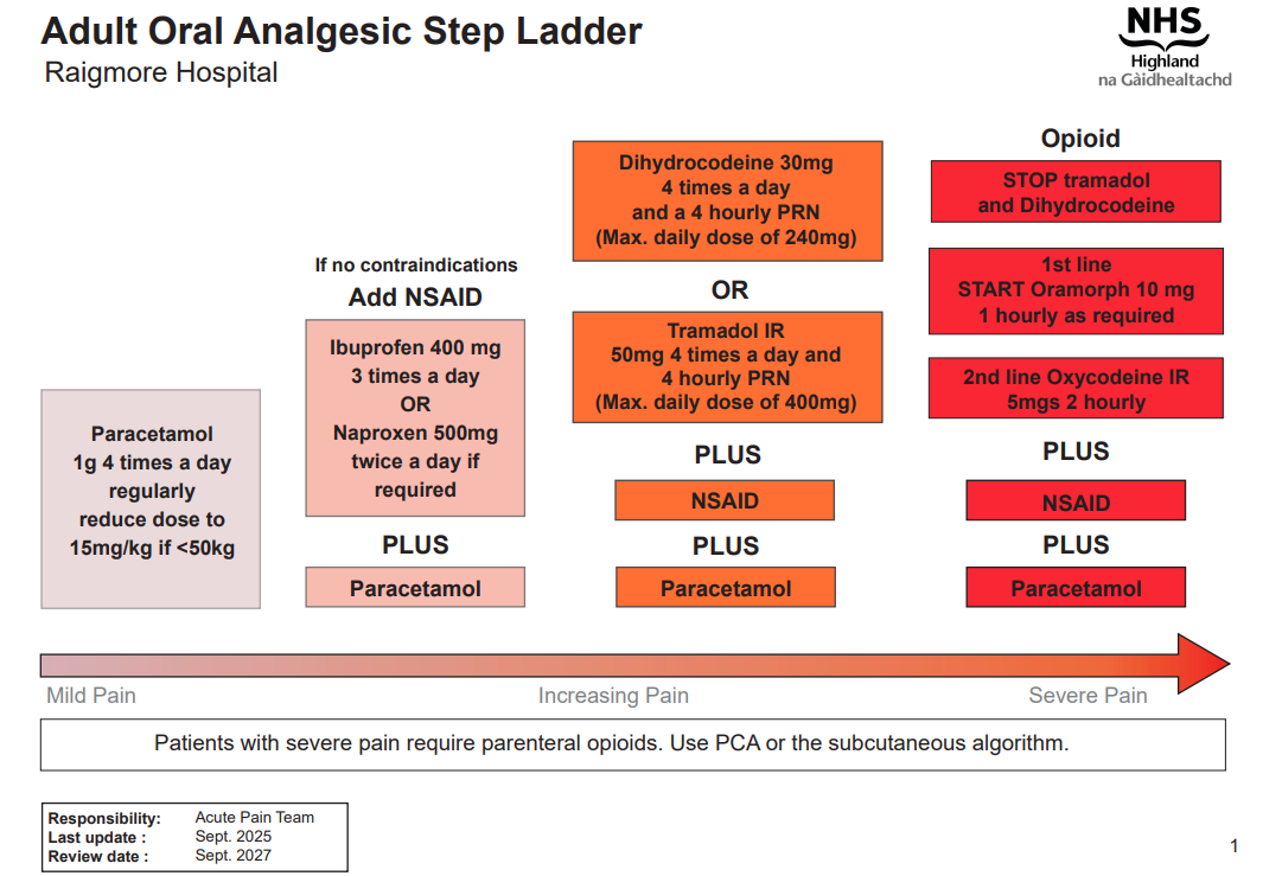
Adult oral analgesia (Guidelines)

What's new / Latest updates
- Removed 'Use ranitidine 150mg bd' from part 2 of NSAID flowchart
- Changed ITU anaesthetist to on-call anaesthetist
Audience
- All NHS Highland
- Primary and Secondary Care
- Review analgesia regularly, at least once a day
- Use the oral route whenever possible.
- Give paracetamol and NSAIDS regularly and opioids PRN.
- When changing from one route of administration to another, use "step-over" doses (equipotent) until you can assess the effect. Later you can change to "step-down" drugs (less potent)
- Avoid the use of compound analgesia e.g. co-codamol
Please remember the side-effects of NSAIDs and stop them if the patient develops dyspepsia or renal impairment.
Part 1
Part 2
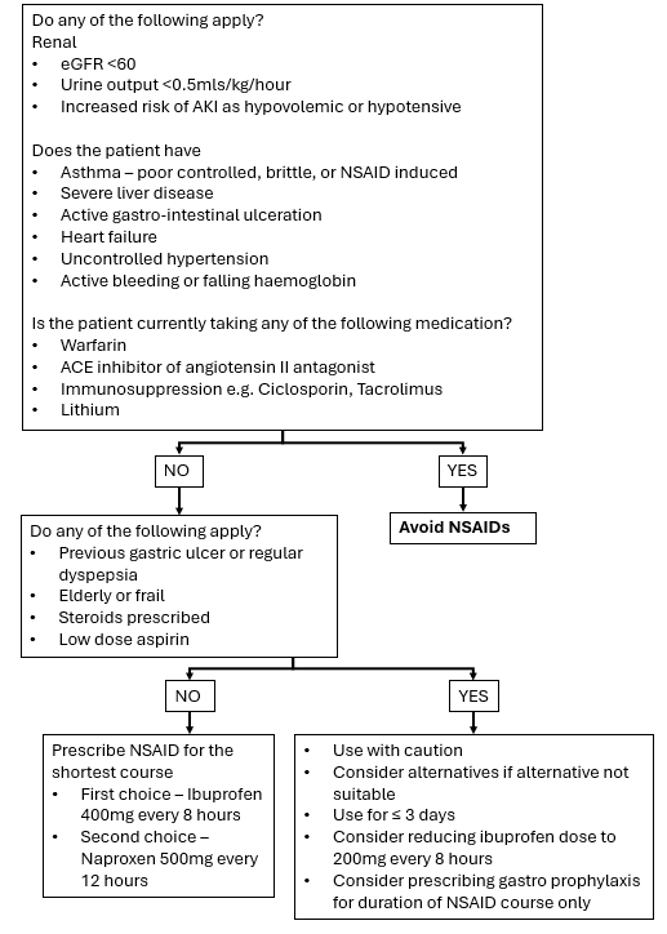
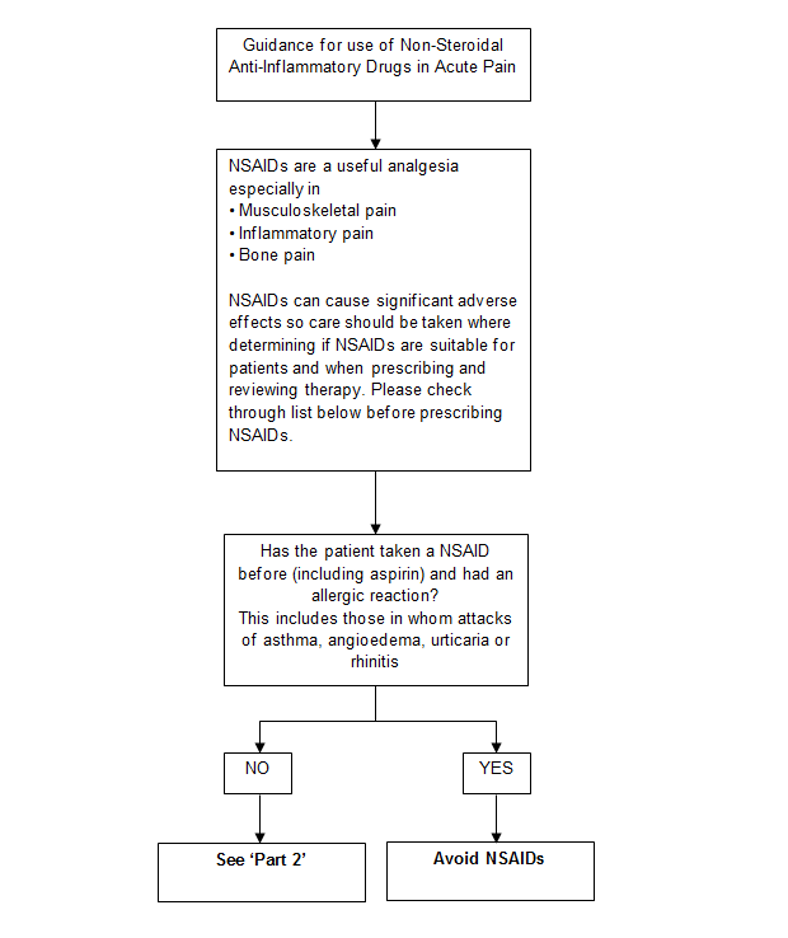
Please refer to NSAID guidelines (see resources).
- In the elderly use a reduced dose and longer dosing interval.
- Patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (see acute pain management in adults with renal impairment) or liver impairment may need a reduced dose and a longer dosing interval.
- In patients with constipation is a problem, ensure stimulant laxatives are prescribed. e.g senna tablets
Remember unexpected pain must be investigated for other causes, especially if the analgesia prescribed becomes ineffective. The patient's condition can change.
Oral Opioids
-
Combination of opioids should not be prescribed or given.
- If you need to change opioids seek advice from Acute Pain Team and/or see Opioid Conversion Chart in the BNF or Palliative Care Formulary.
-
The most common side effects of opioids are:
Constipation:
Laxatives may need to be prescribed. Use with caution if patient has had bowel surgery. Encourage a high fibre diet and adequate fluid intake. Assess for other causes. Older adult inpatient management of constipation
Nausea and vomiting:
An anti-emetic should be prescribed and administered. See PONV guidelines.
Itching:
Assess cause – may not be opioid. Ondansetron can help or low dose naloxone.
Respiratory depression:
If respiratory rate is less than 7 per minute and/or sedation score is 3:
- Contact medical staff, clinical nurse practitioner or the Acute Pain Nurse.
- Administer 10litres/min of oxygen via Hudson face mask.
- Give naloxone (see naloxone guidance)
CAUTION WITH THE FOLLOWING PATIENTS
-
Use a reduced dose with a longer dosing interval in the elderly.
-
Refer to the acute pain management in adults with renal impairment
-
Contact acute pain team for advice on patients with severe liver impairment.
At Raigmore Hospital the Acute Pain Team includes:
Consultant Anaesthetist - Department of Anaesthesia
Clinical Nurse Specialists, Acute Pain Service
Senior Pharmacist - Pharmacy Department
Advice can be sought in office hours - 08.00 – 16.00 (page 1003 or 6056)
Out of hours please contact the on-call anaesthetist.
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| ACE inhibitors | Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| IR | Immediate release |