
Flowchart adapted from NICE guideline [NG136] and 2018 ESC/ESH Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension
- ABPM: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
- HBPM: Home blood pressure monitoring.

06/02/2025:
Sample Template: Home blood pressure monitoring form (NHS Highland intranet access required)
See BNF or manufacturer's information for full prescribing details.
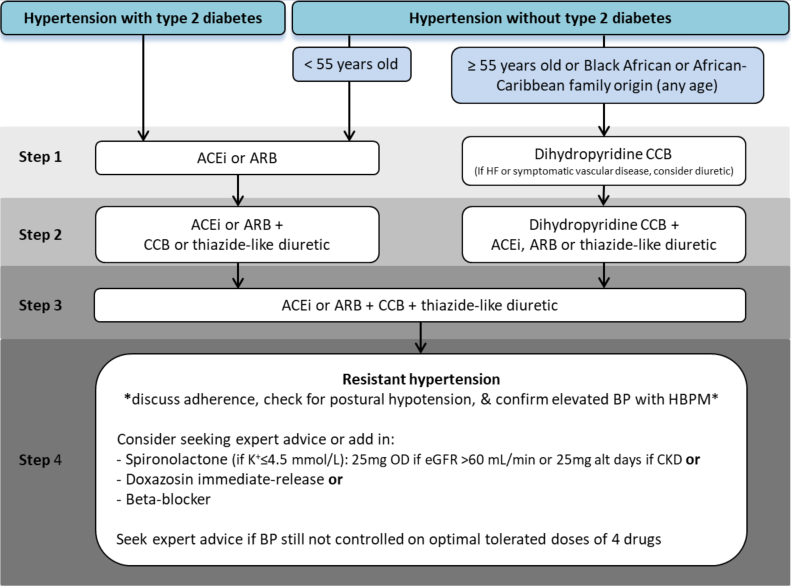
Flowchart adapted from NG136 and SIGN 149
|
Medicine |
Baseline investigation |
After initiation / dose change |
| ACEi/ARB |
U&Es & BP |
U&Es after 2 weeks |
| Beta-blockers |
HR & BP |
HR and BP after 1 to 2 weeks |
| Thiazide-like diuretics |
U&Es & BP |
U&Es and BP after 1 to 2 weeks |
| Spironolactone |
U&Es & BP |
U&Es and BP after 1 week |
The Sick Day Rule cards have been produced to aid patients in understanding which medicines they should stop taking temporarily during illness (e.g. vomiting, diarrhoea and fever) that can result in dehydration
| Indication | Age (years) | ACR (mg/mmol) |
Target BP Clinic (mmHg) |
Notes |
| Hypertension | <80 | NA | <140/90 | |
| ≥80 | NA | <150/90 | ||
| Hypertension AND Diabetes | <80 | <70 | <140/90 |
ACEi or ARB should be used first line, unless contraindicated |
| ≥70 | <130/80 | |||
| ≥80 | NA | <150/90 | ||
| Hypertension AND CKD | NA | <30 | as per hypertension |
ACEi or ARB should be used first line if ACR >30 mg/mmol, unless contradicted |
| 30 to 69 | <140/90 | |||
| ≥70 | <130/80 | |||
|
Hypertension AND Diabetes AND Eye / Cardiovascular / Kidney disease |
NA | NA | <130/80 |
Microalbuminuria: ACR >2.5mg/mmol for males or >3.5mg/mmol for females on 2 or 3 morning samples ACEi or ARB should be used first line if ACR>3 mg/mmol, unless contraindicated |
| Hypertension AND Stroke / TIA | NA | NA | <130/80 | Acute treatment and secondary prevention of transient ischaemic attacks (TIA) and ischaemic stroke (Guidelines) |
If diabetic, 10 year risk of CVD is ≥20%, or a strong family history of premature vascular disease, recommend lipid-regulating therapies.
Use in secondary prevention only.
It is recommended that a CVD risk assessment is offered at least once every five years in adults over the age of 40 with no history of CVD, familial hypercholesterolaemia, CKD or diabetes and who are not being treated to reduce blood pressure or lipids.
Provide an annual review for adults with hypertenson. Key information:
The most common use of Connect Me is within primary care, where GPs and practice nurses enrol patients with hypertension or suspected hypertension.
Connect Me contacts the patient twice a day to ask for blood pressure readings. The patient takes their own blood pressure and sends the reading back to Connect Me. If their BP reading is concerning, Connect Me may respond with some advice about what they should do.
With Connect Me, patients have a choice of communication methods depending on the technology they have access to or are most comfortable with:
For diagnosis of high blood pressure, patients will be asked for readings every day. Once diagnosed they will only be asked for readings on two days a week or possibly just one day a month.
The patient's GP will be sent a report of the patient's BP readings at regular intervals, so they can assess whether the patient has high blood pressure or can check whether their medication is working effectively, without the patient having to make repeated visits to the surgery.
Connect Me resources for clinicians and patients: Connect Me (NHS Highland intranet access required)
Contact information: nhsh.connectme@nhs.scot
In Highland, most of our Connect Me services are provided by the Inhealthcare remote health monitoring platform.
Lifestyle advice:
High risk: History of haemorrhagic/ischaemic stroke, TIA, Diabetes, CKD, target organ damage, known CVD
Target organ damage:
Postural hypotension: A sustained reduction of systolic blood pressure of at least 20mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of 10mmHg within 3 minutes of standing, or of tilting the body (with the head up) to at least a 60° angle on a tilt table
Resistant hypertension: Blood pressure that is not controlled to goal despite adherence to an appropriate regimen of three antihypertensive drugs of different classes (including a diuretic) in which all drugs are prescribed at suitable antihypertensive doses and after white coat effect has been excluded. Blood pressure that requires at least four medications to achieve control is considered controlled resistant hypertension
Masked hypertension: Blood pressure measurements are normal in clinic but are higher when taken outside the clinic using average ABPM/HBPM.
White coat hypertension: Blood pressure that is unusually raised during consultations with clinicians but is normal when measured in ‘non-threatening’ situations. It occurs in about 15-30% of the population.
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| ABPM | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring |
| ACEI | ACE inhibitor |
| ACR | albumin : creatinine ratio |
| ARB | angiotensin II receptor blocker |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BP | blood pressure |
| CCB | calcium channel blocker |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| ECHO | echocardiogram |
| FBC | full blood count |
| HbA1c | haemoglobin A1c |
| HBPM | home blood pressure monitoring |
| HR | heart rate |
| LFTs | liver function tests |
| LVEF | left ventricular ejection fraction |
| PCR | protein : creatinine ratio |
| TIA | transient ischaemic attack |
| U&Es | urea and electrolytes |