Objective
- To allow rapid and appropriate response to major haemorrhage (MH).
- To ensure appropriate communication between clinical area and the BTS laboratory
- To provide quick and effective delivery of blood components to patients with MH
Target Population
- Patients admitted to Raigmore hospital
- Adults (age over 14; weight over 40 Kg), including obstetric patients
- Children and neonates
Definition of massive bleeding
Haemorrhagic SHOCK with ongoing major blood loss due to any underlying cause
Adults
- blood loss > 150mL/min
- 50% blood volume loss in < 3 hours
- 4 units RBC in < 4 hours.
* Total blood volume of an adult 70mL/kg
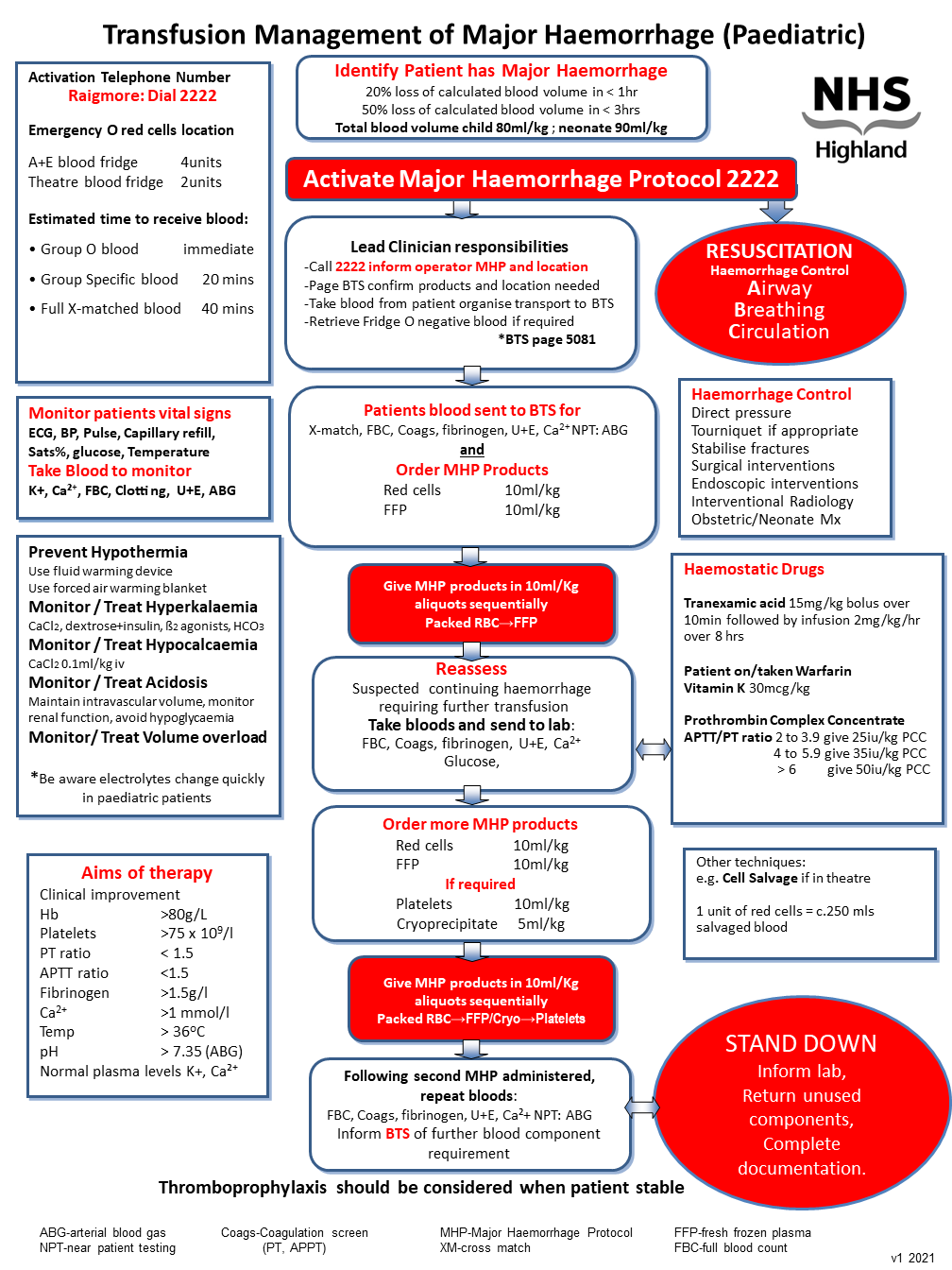
Paediatric
- 20% loss of calculated blood volume in < 1hr
- 50% loss of calculated blood volume in < 3hrs
*Total blood volume of a child 80mL/kg
*Total blood volume of a neonate 90mL/kg
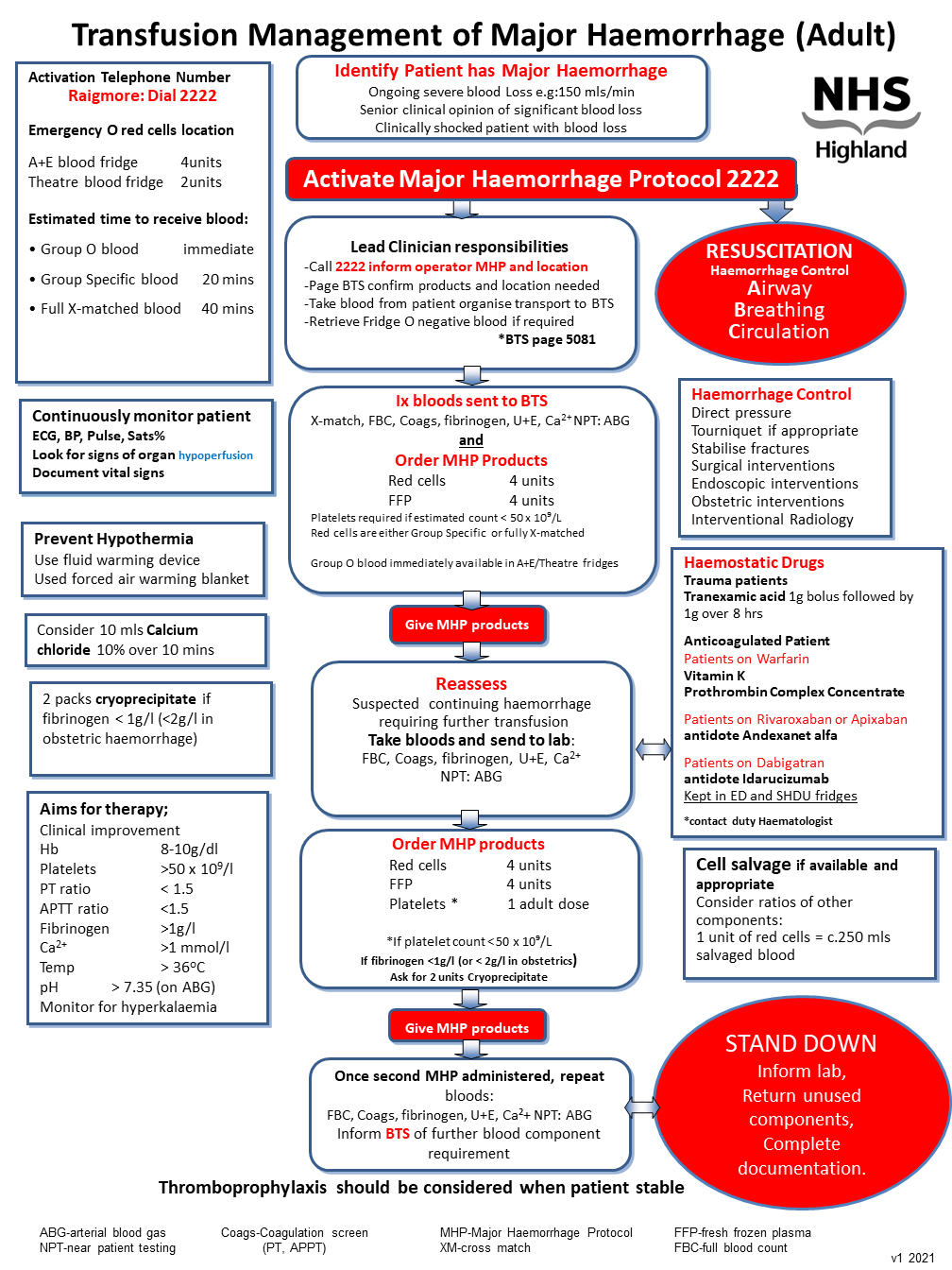
Trigger for Major Haemorrhage Protocol (MHP) activation
Senior clinician determines that the patient bleeding fulfils the definition of a major haemorrhage
Responsibilities of the lead clinician
The responsibilities of the lead clinician themselves or by delegation, are,
- Resuscitation of the patient; A, B, C and administration of blood components
- Activating the Major Haemorrhage Protocol; Call switchboard 2222
- Contact BTS; Page 5081 confirm products required and location
- Definitive management; May include contacting endoscopy, theatre, obstetric team
- Blood sample taken and transported; Patient blood sample sent to BTS laboratory
- Documentation; Ensure events are documented and adherence to blood and blood product administration policy is adhered too.

 For printable PDF click
For printable PDF click