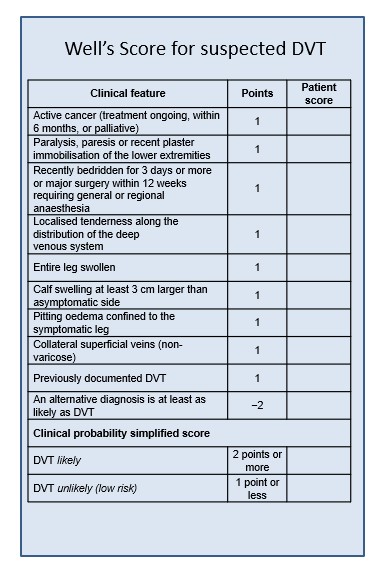
Commence rivaroxaban (unless contra-indicated) for creatinine clearance over 30: 15mg b.d. for 3 weeks and 20mg daily thereafter (unless contraindicated)
- if eGFR below 30ml/min please use warfarin or LMWH as clinically indicated***
- Provide appropriate lifestyle and bleeding advice and education (provide patient leaflet and card).
- Remember to advise the patient to take rivaroxaban with food as this increases bioavailability significantly.
If contraindications to rivaroxaban - use LMHW and warfarin
Contraindications to rivaroxaban:
- Patients requiring anticoagulation beyond 12 months
- ***Patients with creatinine clearance below 30ml/min
- Active cancer/chemotherapy patients - commence on a course of LMWH and discuss with oncology
- Pregnant patients:
- twice daily dose dependant on early pregnancy weight
- continue LMWH treatment throughout pregnancy nad breast-feeding for at least 6 months
- Hepatic disease associated with coagulopathy - discuss with consultant of GI registrar
- HIV or hep C patients taking NNRTIs or protease inhibitors
- commence on dalteparin/warfarin and discuss with the HIV team
- If unsure about current therapy check clinical letters on Portal (ECS unreliable for re:HIV and hep C meds)
- Co-prescription of strong inhibitors of both cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) (enhanced effectiveness)
- e.g. azole antifungals (ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole and posaconazole) and HIV protease inhibitors
- Co-prescription with strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inducers (reduced effectiveness)
- e.g. rifampicin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital or St. John's wort
- In patients at extremes of weight (BMI below 18.5kg/m2 or above 30kg/m2)
- For a complete list of drug interactions please see BNF appendix 1 (anticoagulants) and relevant SPC