The Assessment and Management of Acute Exacerbation of COPD in Secondary Care
If you have identified a patient as having an acute exacerbation of COPD:
Basic investigations
Chest X-ray, ABG, ECG and routine bloods, sputum cultures if the patient is productive of sputum and blood cultures if the patient is pyrexic.
Main management points:
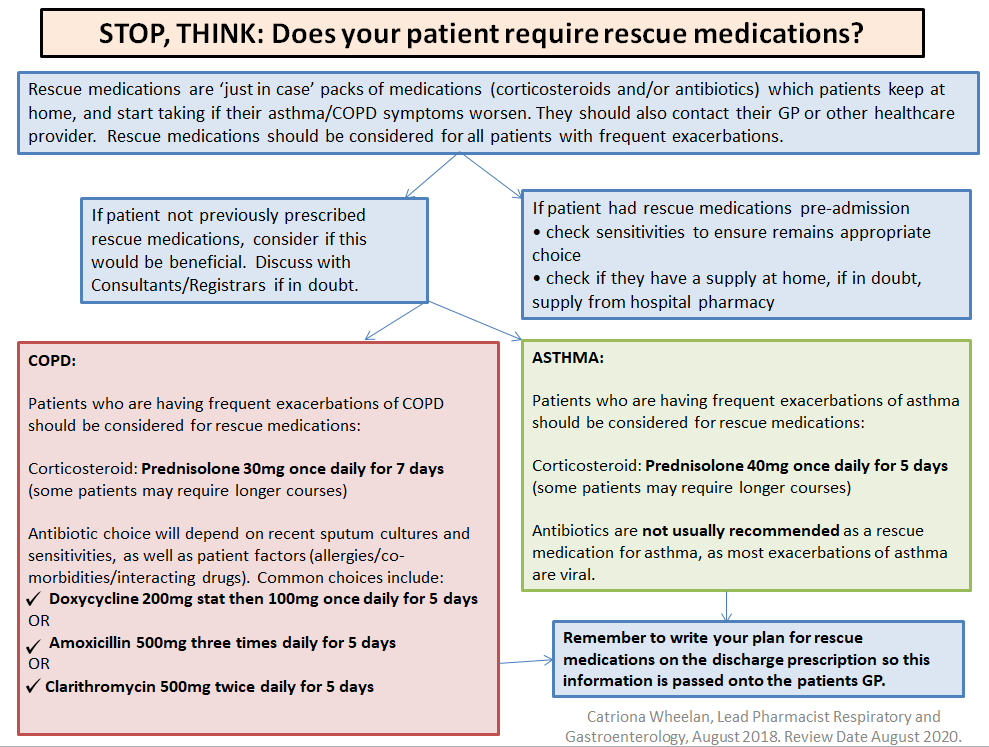
In the absence of significant contraindications prescribe oral Prednislone 30mg for 5 days.
If you think the exacerbation is infective follow antimicrobial advice:
In addition prescribe nebulised or inhaled bronchodilators depending on symptom severity (most hospitalised patients with COPD will need nebulised therapy for the initial period of treatment, usually prescribed regularly eg. four times a day, in addition to as required):
- Generally we recommend 5mg nebulised salbutamol and 500 micrograms ipatropium
- If a person with COPD is hypercapnic or acidotic the nebuliser should be driven by compressed air rather than oxygen (to avoid worsening hypercapnia). This should be specified in the prescription. If oxygen therapy is needed, administer it simultaneously by nasal cannulae.
- If patient is on a LAMA (example inhalers would include trelegy ellipta, incruse ellipta, anora elllipta, trimbow, spiolto or spiriva) then do not prescribe regular ipatropium nebulisers and these patients should be continued on their usual inhaler.
- Ideally a mouthpiece rather than face mask should be used for nebulised ipatropium due to potential for eye complications
Oxygen Therapy
- Aim for 88-92% using venturi masks to deliver controlled oxygen therapy until you have an ABG result
- If the ABG shows hypercapnia, or a high bicarbonate level suggesting chronic CO2 retention, then aim for 88-92%
- If the patient had saturations before they were unwell <94%, then they should also be aimed 88-92%
- If they have a normal CO2, then you can aim 94-98%
- If they are hypercapnic and acidotic despite optimal medical therapy then the patient should have senior medical review for consideration of NIV, which should be delivered in a level 2 area
Discharge
We generally recommend that patients are off nebulised bronchodilators for 24 hours before discharge. There are a number of other interventions which should be considered at the time of discharge, ideally with delivery of a COPD discharge bundle. These interventions should include:
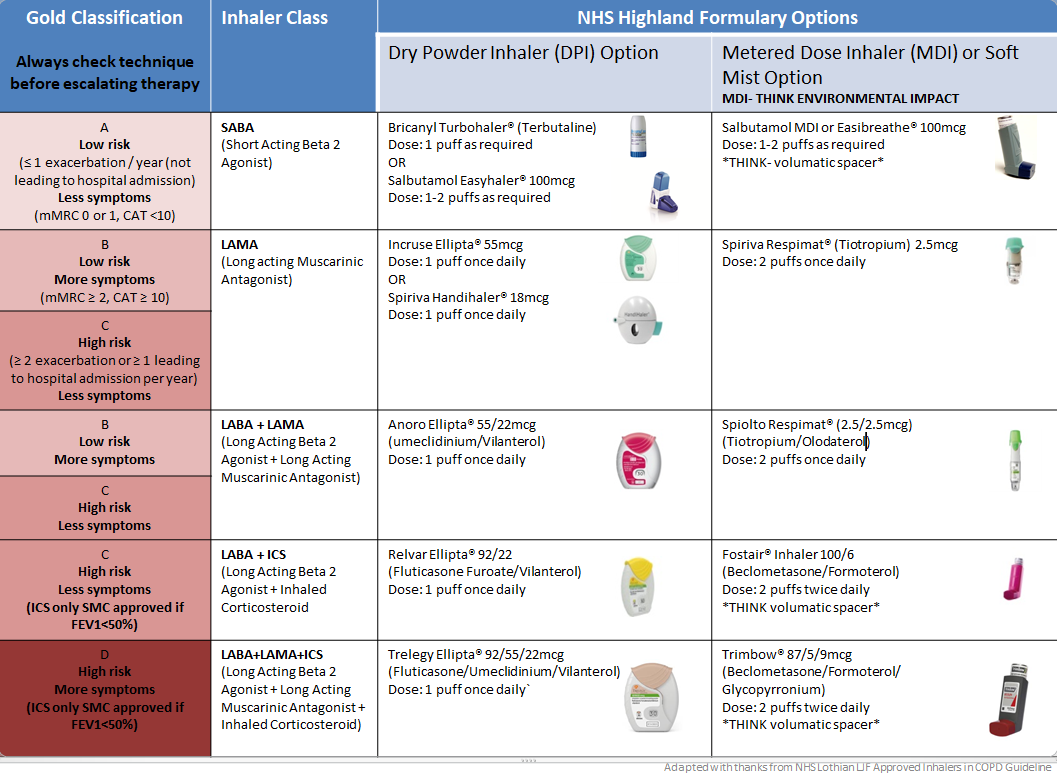
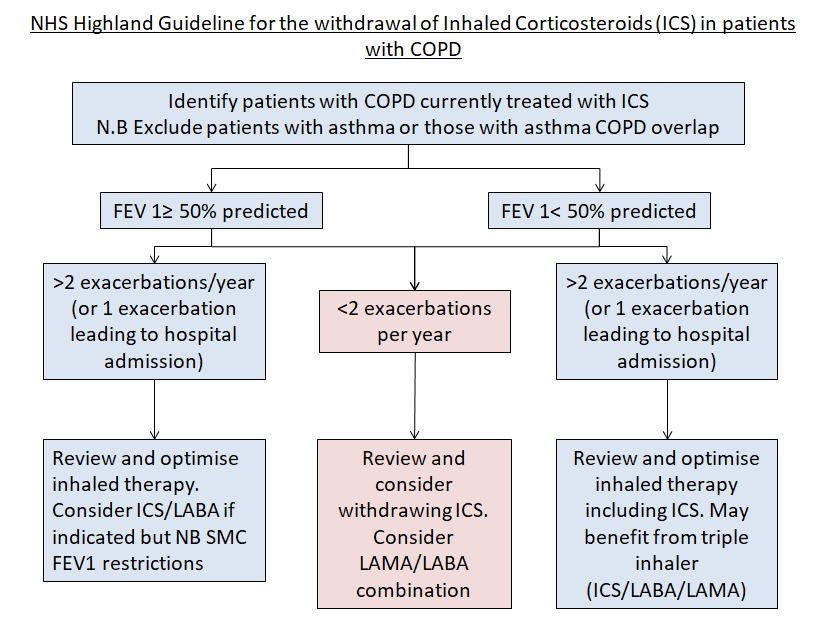
- Optimising their regular inhaled maintenance therapies and reviewing inhaler technique. If there has been an escalation in symptoms outwith the time they have had an acute exacerbation, or if they are having recurrent exacerbations consider if there is a need to change their regular inhaled therapy. See “Inhaled Therapy for COPD” for a clearer understanding of the different inhalers and options.
- Considering what follow up the patient requires (if any). All discharges should be referred to the community respiratory team (nhsh.communityrespiratoryteam@nhs.scot). If a patient is having frequent exacerbations then community support may help optimise their care and may provide the opportunity to have anticipatory care plan discussions.
- Consider whether smoking cessation referral is required and discuss this with the patient. Smoking cessation guidelines can be found here: Smoking cessation (Guidelines)
- Consider if referral to pulmonary rehabilitation will be beneficial for the patient, for more information: https://tam.nhsh.scot/for-healthcare-professionals/therapeutic-guidelines/respiratory/pulmonary-rehabilitation/
- Offer the patient access to patient education and self management resources:
- MyLungsMyLife
- British Lung Foundation
- Chest Heart and Stroke Scotland
- Self-management plans 'Traffic Lights for COPD' are free to order or can be printed
- Use self-management checklist as an aide-memoire
The most recent guideline which covers the management of COPD exacerbation in the UK is the 2018 NICE guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management which can be accessed at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng115