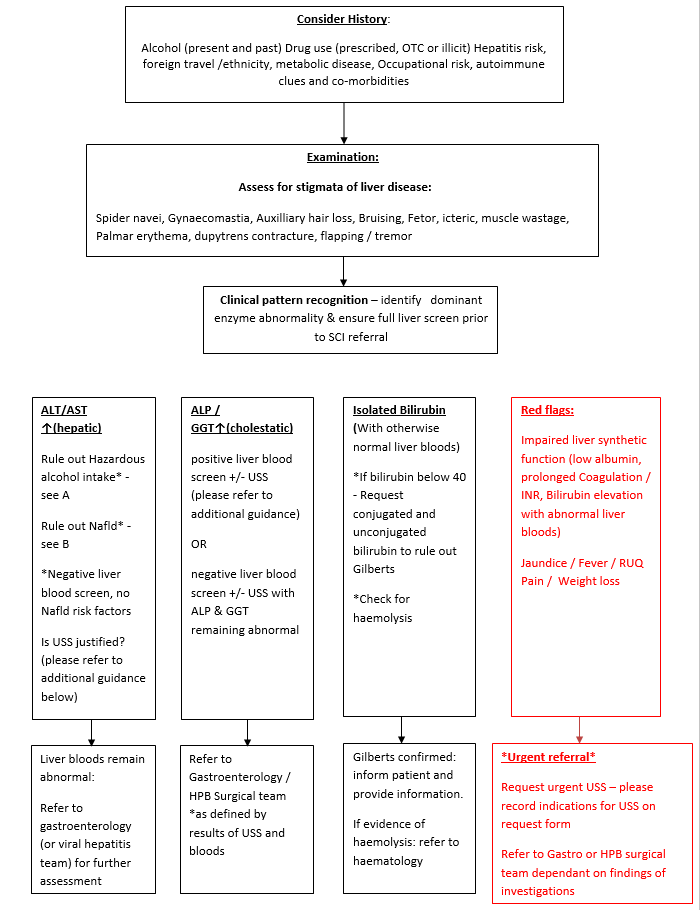
Full liver screen includes USS, liver bloods including GGT and AST, Hep B surface antigen, Hep C antibodies, AMA, ASMA and ANA antibodies, serum immunoglobulins and simultaneous ferritin and transferrin saturations
NICE Guideline
BSG Guideline
Gilberts Patient information
Additional information: When to request USS as part of a full liver screen.
Historically, an abdominal ultrasound has been requested as part of the full liver screen. In line with BMUS and local guidelines agreed with NHS Highland Radiology department, please be aware that an ultrasound may not always be justified as part of first-line investigations.
When is an USS justified as part of full liver screen:
- ALT or ALP is greater than 2.5 x ULN or rising suddenly
- Patient has signs and symptoms of advanced liver disease (Please see referral pathway for abnormal liver bloods in over 16s)
- Suspicion of biliary obstruction or cholecystitis
- Suspicion of malignancy
Please record relevant information on Radiology request form:
- Which LFTs are deranged, by how much and for how long?
- Patient symptoms (including weight loss)
- A specific diagnosis (if known)
When an USS is NOT justified as part of full liver screen:
- Isolated single liver enzyme rise (Please see referral pathway for abnormal liver bloods in over 16s)
- Asymptomatic patient with single episode of mild to moderate rise in liver enzymes
- Patient with known high risk factors for NAFLD (type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia) - Where NAFLD is the likely diagnosis, fibrosis risk stratification (pathway B) is more useful than ultrasound.
- Patient on drugs known to cause hepatic enzyme rises (eg. Statins) – please stop drug and repeat liver enzyme tests in 1-3 months
If there is clinical doubt as to whether an USS should be arranged prior to referral to Gastroenterology, please contact livernursespecialists@nhs.scot