- Do not send urine for culture in asymptomatic elderly with positive dipsticks
- Only send urine for culture if two or more signs of infection, especially dysuria, fever greater than 38oC or new incontinence.
- Do not treat asymptomatic bacteriuria in the elderly as it is very common.
- Treating does not reduce mortality or prevent symptomatic episodes, but increases side effects & antibiotic resistance.
Diagnosis of UTI (Guidelines)

|
Urinary Symptoms In Adult Women under 65 Do Not Culture Routinely In sexually active young men and women with urinary symptoms consider Chlamydia trachomatis |
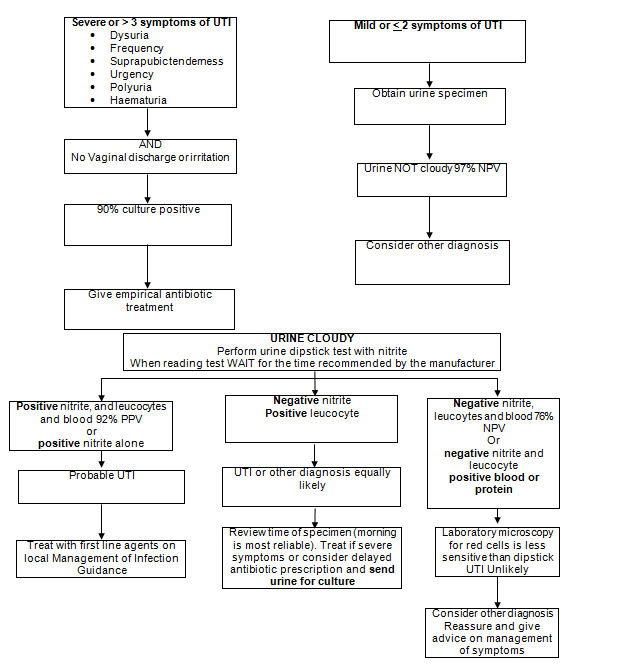
Urinary tract (UTI) (Antimicrobial)
- Do not treat asymptomatic bacteriuria in those with indwelling catheters, as bacteriuria is very common and antibiotics increase side effects and antibiotic resistance.
- Treatment does not reduce mortality or prevent symptomatic episodes, but increase side effects & antibiotic resistance.
- Only send urine for culture in catheterised if features of systemic infection. 1,5,6C However, always:
- Exclude other sources of infection.
- Check that the catheter drains correctly and is not blocked.
- Consider need for continued catheterisation.
- If the catheter has been in place for more than 7 days, consider changing it after starting antibiotic treatment
Do not give antibiotic prophylaxis for catheter changes unless history of symptomatic UTIs due to catheter change.
- Pregnancy:
If symptomatic, for investigation of possible UTI. In all at 1st antenatal visit - as asymptomatic bacteriuria is associated with pyelonephritis & premature delivery. - Suspected pyelonephritis(loin pain and fever).
- Suspected UTI in men.
- Failed antibiotic treatment or persistent symptoms. E. coli with Extended-spectrum Beta-lactamase enzymes (ESBL)are increasing in the community. ESBLs are multi-resistant but usually remain sensitive to nitrofurantoin or fosfomycin.
- Recurrent UTI, abnormalities of genitourinary tract — more likely to have a resistant strain.
Refrigerate specimens to prevent bacterial overgrowth or use specimen pots with boric acid (fill to the line).
- In women: the specimen should be mid-stream. Cleansing with water and holding the labia apart are not essential. Cleansing with antiseptic leads to false negatives.
- In men: the specimen should be mid-stream.
- People with catheters: using aseptic technique, drain a few mL of urine, then collect a sample from catheter sampling port.
Follow-up urine samples are not usually indicated, except when treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy.
(see page 27 of Microbiology Department User Manual)
The following usually indicates UTI in patient with urinary symptoms. 1Higher counts have even higher positive predictive value.
- Single organism greater than or equal to 104 colony forming units (CFU)/mL1
- Or greater than or equal to 105 mixed growth with one predominant organism
-
Or Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus saprophyticus greater than or equal to 103(CFU)/mL1
Do not treat asymptomatic bacteriuria in the elderly as it does not reduce mortality or prevent symptomatic episodes.
White blood cells
White cells greater than or equal to 104/mL are considered to represent inflammation.
In adults ‘no white cells present’ indicates no inflammation & reduces culture significance.
Pregnancy is associated with physiological pyuria.Sterile pyuria
In sterile pyuria consider Chlamydia trachomatis(especially if 16 to 24 years), other vaginal infections, other non-culturable organisms, including TB or renal pathology. Epithelial cells/mixed growth
Presence indicates perineal contamination, which reduces significance of culture. Red cells
May be present in UTI, patients with persistent haematuria post UTI should be referred - see Urology Guidelines on Occult or non visible Haematuria
Lab microscopy for red cells is less accurate than dipstick due to red cell lysis in transport.
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| UTI | Urinary tract infection |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |