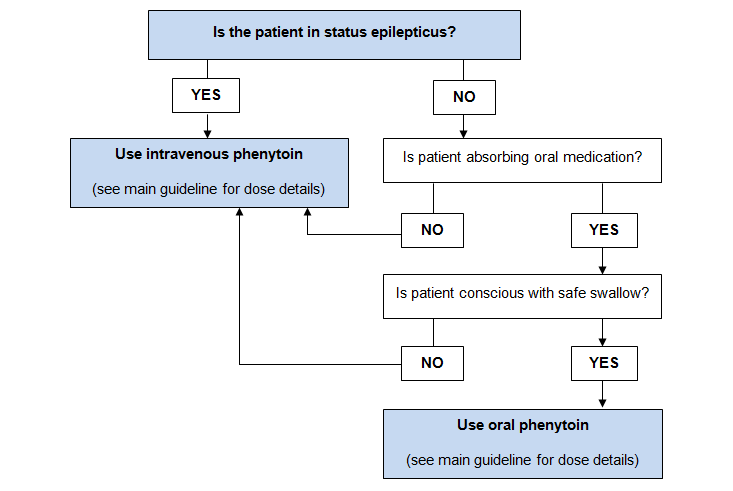
If the patient has not already received phenytoin then give:
- Intravenous phenytoin sodium 18mg/kg (see Table 1 below). Ensure ECG, blood pressure and respiratory function are monitored throughout the duration of the infusion.
Table 1: Intravenous phenytoin loading dose
Actual body weight (kg) | Intravenous loading dose (mg) | Volume of intravenous phenytoin (mL) (vial = 250mg/5mL) |
35 to 44 | 700 | 14 |
45 to 54 | 900 | 18 |
55 to 64 | 1100 | 22 |
65 to 74 | 1250 | 25 |
75 to 84 | 1450 | 29 |
85 to 94 | 1600 | 32 |
>94 | 1800 | 36 |
Intravenous phenytoin administration
- Give phenytoin over 30 to 40 minutes (rate <50mg/minute). In patients who are elderly, or have pre-existing cardiac disease, give phenytoin over 60 minutes. NB: Adminstration should commence immediately after the mixture has been prepared and completed within 1 hour.
- Ideally, administer undiluted via a syringe pump through a large gauge needle or intravenous catheter into a large forearm vein.
- If dilution is essential, mix with 100 to 250mL sodium chloride 0·9% to a final concentration of <10mg/mL, and administer by infusion pump. Stability of the diluted solution is limited and precipitates may form. Use the solution immediately, ideally with a 0·2 to 0·5micron in-line filter.
- To avoid local venous irritation, inject sterile sodium chloride 0·9% through the vein or catheter before and after each phenytoin infusion.
- Do not administer as a continuous infusion.
- Continuous ECG and blood pressure monitoring is essential during infusion.