Principal/Indication
The first line screening test to investigate patients with hypertension (and hypokalaemia) for primary hyperaldosteronsim (Conn’s Syndrome) is a random aldosterone/renin ratio (ARR). This is less affected by drug therapy, diurnal variation and patient position than aldosterone and renin alone. The initial screening test can usually be done on treatment.
Preparation and procedure
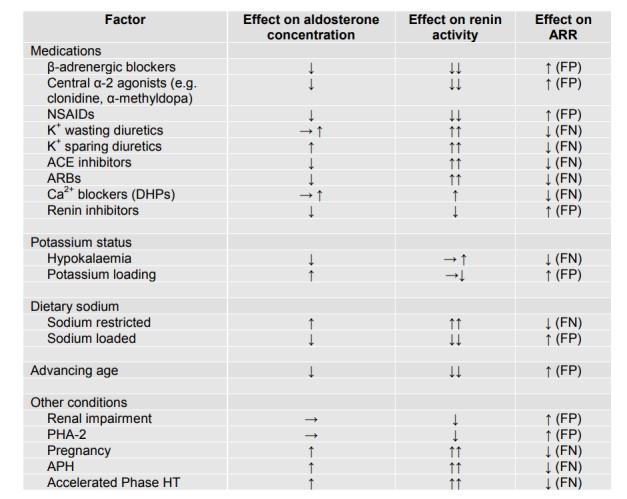
- Whilst optimal to perform this test on no interfering anti-hypertensive drug therapy, this is often impractical and may result in significant risk to the patient. Therefore, with the exception of the mandatory medication withdrawals listed in Table 1, this initial screening test can be performed on anti-hypertensive therapy provided these medications are noted and the requesting clinician is aware of their potential effects on aldosterone and/or renin.
It is the responsibility of the physician co-ordinating the investigations to oversee the withdrawal of the medication and to ensure that the patient has a clear plan for when to restart previous medications. - Correct hypokalaemia and do not restrict salt intake prior to the test.
- Patient should be adequately hydrated.
- Ideally perform at 9-10 am, unless undertaking ad hoc testing in clinic.
- Ensure patient has been ambulant during a 2 hours period prior to the test.
- Patient should then sit upright for 15 minutes.
- Inform lab of test.
- Complete laboratory request forms for renin & aldosterone & U&Es
- Take blood for U&Es (brown gel tube), renin and aldosterone (2 x red ETDA tubes) and send to lab immediately, not on ice.
- End test.
Interpretation
- The aldosterone reference range is 130-800pmol/l. Plasma renin is reported as Plasma Renin Concentration (PRC) therefore the Aldo/PRC should be used to guide further investigation for hyperaldosteronism.
- An aldosterone to renin ratio (ARR) of < 35 is normal
- An aldosterone to renin ratio (ARR) of ≥ 35 cannot exclude primary hyperaldosteronism (especially if plasma aldosterone level >410 pmol/l)
- If the initial random ARR is abnormal and the patient was still on drugs which are known to interfere with the ARR then the test should be repeated off the offending drugs, as per Table 1, substituting with doxazosin and/or twice daily verapamil MR if required. Double check liquorice and chewing tobacco intake. If the second test off interfering drugs is abnormal proceed to the saline infusion test.
- If the patient has spontaneous hypokalaemia, and significant biochemical aldosterone excess (>550 pmol/L) and undetectable PRC then confirmatory testing (saline infusion) is not required.