The characteristic clinical manifestations of RPOC may include heavy or prolonged uterine bleeding and pelvic pain. Signs of infected RPOC can commonly include pyrexia, offensive discharge or uterine tenderness.
Retained Products of Conception (RPOC) (677)

Objectives
To standardise the management options for women diagnosed with RPOC
Audience
All healthcare workers involved in the care of women with pregnancy complications
Please report any inaccuracies or issues with this guideline using our online form
The term retained products of conception (RPOC) refers to placental, membranes and/or fetal tissue that remains in the uterus after a spontaneous pregnancy loss (miscarriage), termination of pregnancy or following a preterm/term delivery. The presence of RPOC after a spontaneous pregnancy loss distinguishes a complete from an incomplete miscarriage.
Any patient who is haemodynamically unstable or clinically unwell requires urgent medical review, NEWs monitoring, IV access and resuscitation (including FBC, G&S as minimum). Consider vaginal swabs and administration of antibiotics if sepsis is suspected.
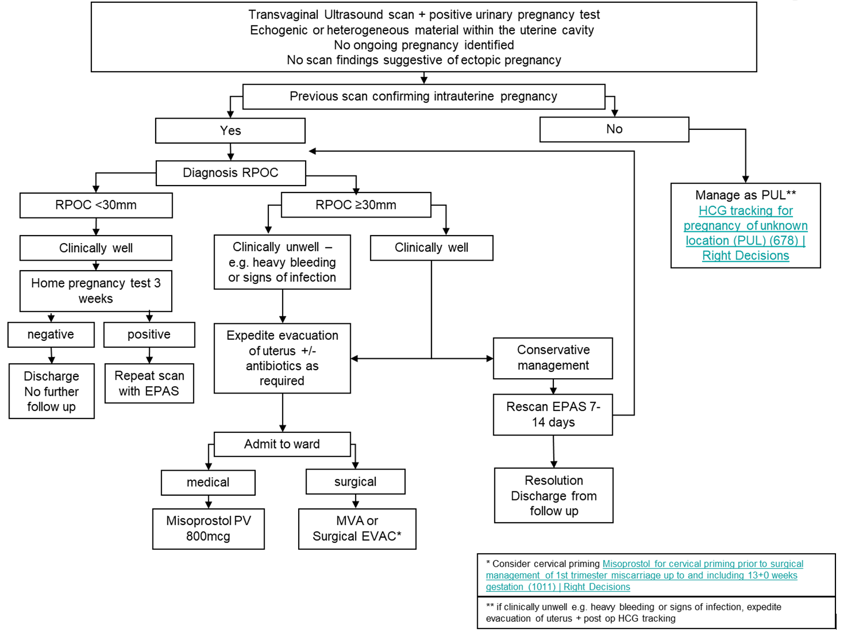
The management of RPOC is outlined in the flow diagram in Appendix 1.
A speculum examination should be considered to assess bleeding and look for RPOC which could easily be removed. Consider obtaining vaginal swab for microbiology +/- NAAT testing for chlamydia.
Conservative Management
This can be considered where women are clinically well.
Where RPOC diameter is <30mm, management at home with a repeat home pregnancy test after 3 weeks is appropriate. If test remains positive, further review through EPAS/ Sandyford TOPAR clinic should be offered as appropriate.
Where RPOC diameter ≥30mm, women who opt for conservative management should be offered a repeat ultrasound scan in EPAS/Sandyford TOPAR clinic after 7-14 days as appropriate.
Medical management
Where women opt for medical management, they should be admitted to hospital and a single dose of Misoprostol 800mcg should be administered (vaginal or sublingual) [1]. It is estimated 60-70% of women will have complete resolution following medical management [2,3].
Patients should be observed for up to 4 hours.
- If pregnancy tissue is visualised and bleeding settled
Patient may be discharged home and advised to undertake and home pregnancy test in 3 weeks and contact EPAS/ Sandyford TOPAR clinic if remains positive.
- If no pregnancy tissue is visualised, a speculum examination should be undertaken.
If bleeding is settled, patient can be discharged home with advice to perform a home pregnancy test after 3 weeks. They should be advised that tissue may pass at home and to contact the hospital ward or attend A&E if bleeding is heavy or they feel unwell or have symptoms of infection.
Patients may also be offered repeat medical management or surgical management as they wish.
Surgical Management
Where women opt for manual vacuum aspiration MVA, please see local guideline. Manual Vacuum Aspiration (MVA) for treatment of miscarriage and retained pregnancy tissue (1078) | Right Decisions
Where women opt for inpatient or daycase surgical management under general anaesthetic, or in the emergency setting to control heavy bleeding or treat infection, please see local guideline. Surgical Management of First Trimester Miscarriage (894) | Right Decisions
Where RPOC is diagnosed following birth in labour ward (including midtrimester loss, stillbirth, preterm and term births), management should be co-ordinated though maternity services. Surgical management in these cases can associated with higher risk of uterine perforation and bleeding, and senior medical staff should be involved with the procedure.
This is pregnancy tissue and should be processed as such. RPOC should be sent for histopathology. Please see local guideline for details and forms required. Fetal Tissue - handling and disposal (up to and including 23+6 weeks gestation) (340) | Right Decisions
Rhesus status should be checked and Anti-D administered as per local guideline. Anti-D Immunoglobulin Administration Following Potentially Sensitising Events and Routine Antenatal Anti-D Prophylaxis in RhD Negative Women (559) | Right Decisions
All women should have a VTE assessment performed according to local guidelines. VTE prophylaxis should be administered as required.
Most women will not require further follow up
However, the patient should be advised to re-contact their base clinic (EPAS or Sandyford TOPAR clinic) in the following situations.
- Bleeding fails to settle after 3 complete weeks from being diagnosed, even if pregnancy test negative. (Requires rescan)
- If pregnancy test remains positive after 3 weeks. (Requires rescan + HCG)
- If there are signs of infection e.g. raised temperature, foul smelling discharge, generally feeling unwell. (Requires rescan and infection screening)
- Contraception should be offered and provided as needed.