Offer face to face appointment in an appropriate clinic, i.e TOPAR/ GU Complex / Urgent Care or in the case of post partum infection refer back to Obstetric services.
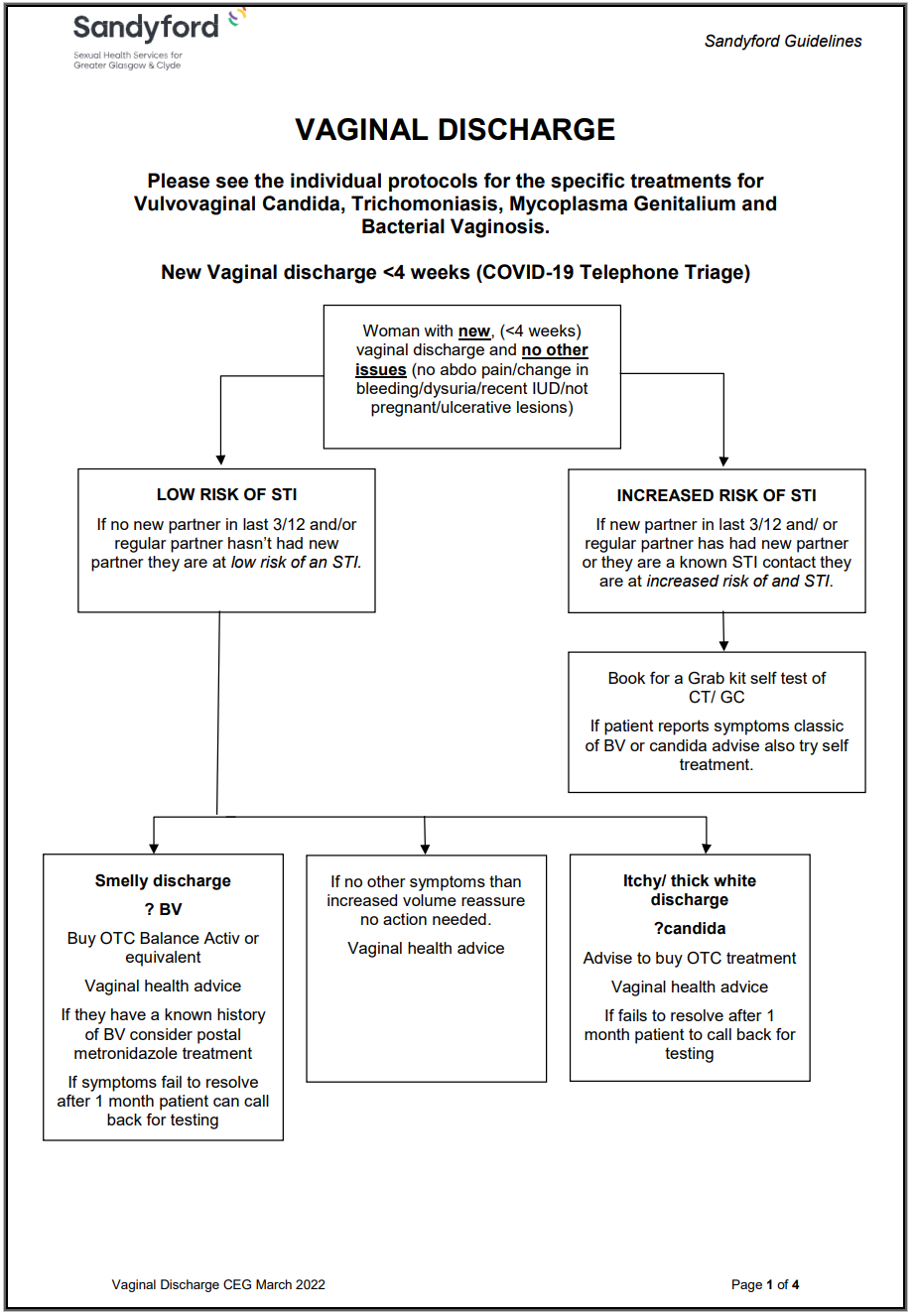
Vaginal Discharge Management (317)

Please report any inaccuracies or issues with this guideline using our online form
- Examination and pH
- Microscopy (*dry slide for Gram staining and **wet prep)
- Endocervical GC culture (if plates available)
- High Vaginal Swab (⁂HVS) if recurrent or persistent
- Vulvovaginal CT/GC NAAT
Management of results (please refer to appropriate guidelines)
- Trichomonas Vaginalis (TV) seen – TV
- pH >4.5 +/- Clue cells and abnormal flora – BV
- pH <4.5 +/- Yeast cells – Candida
- Gram Negative Diplococci (GNDC) seen – GC
- High AV score: discuss with senior
*Dry slide (vaginal and cervix) for Gram stain.
**Wet prep taken from the vaginal posterior fornix. Connect a HVS is taken using a charcoal swab for wet prep.
⁂ HVS – taken from lateral vaginal wall. Stored at 4°C for maximum 48 hours.
Microscopy venue: Sandyford Central.
CONNECT: If microscopy requested please leave the registration form of client with the Connect nurse to follow up client with result.
Defined as “Disruption of the lactobacillary (LB) flora, accompanied by signs of inflammation and the presence of predominantly aerobic microflora composed of enteric commensals or pathogens.”
Vaginal Flora Grade – Modified Hay-Ison Score
Grade | Description |
0 | No flora |
I | Normal vaginal flora (LB alone) |
II | Mixed |
III | Abnormal |
IV | Gram positive cocci only |
AV Donder’s Score
This is calculated from a WET film. Not all people who can read slides are trained to do this assessment please confirm on the day. It is based on the following criteria, each given a score from 0-2.
- Lactobacillary (LB) flora
- Number of leucocytes
- Proportion of toxic leucocytes
- Background flora
- Proportion of parabasal cells (epithelial damage)
Severity
- Mild 1-4
- Moderate 5-6
- Severe 7-10
- Scores above 5-6 (moderate) or 7 or higher (severe) require clinician to consider AV as well as other causes for an inflammatory vaginitis, including TV and Group A streptococcus.
- Always take a HVS culture swab (self-taken is fine) if moderate or high AV score.
- No clear evidence base for treatment. Discuss with senior clinician. Consider using clindamycin vaginal cream (covers aerobic organisms) instead of metronidazole
Advice should be given to the client that some factors may affect normal vaginal health causing a disruption to the normal flora and pH.
Some causes of irritation include:
- Antibiotics
- Some types of clothing (tightly fitted/synthetic material)
- Over-washing/bathing douching or the use of shower gels or antiseptic agents, bath oils
- Avoid using feminine hygiene sprays, perfumes or wipes
- Avoid using daily pads or fragranced sanitary products
- Avoid use of flavoured/coloured condoms or lubricant
- Avoid using fabric conditioner and biological washing powder
Advise to wash with water or a soap substitute. Offer and prescribe soap substitutes such as aqueous cream or emulsifying ointments.
Consider providing a Sandyford genital skin information leaflet via SMS

