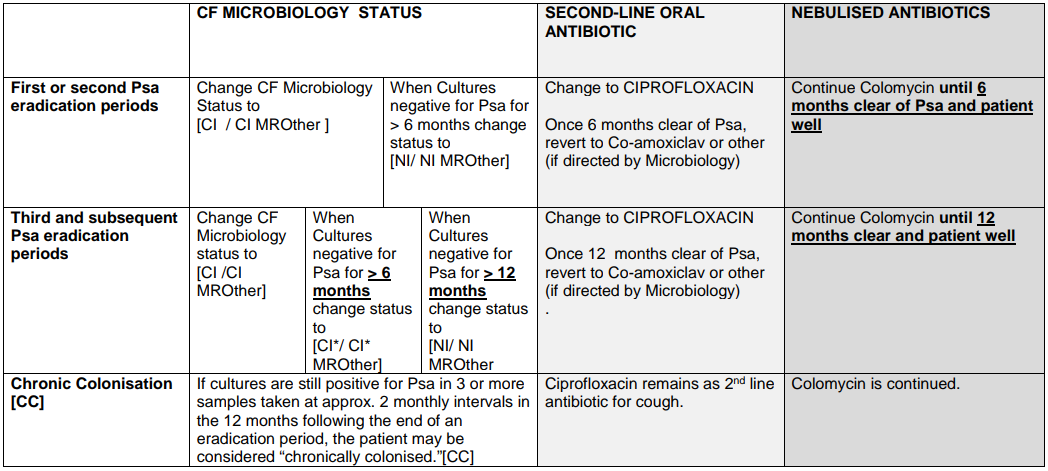
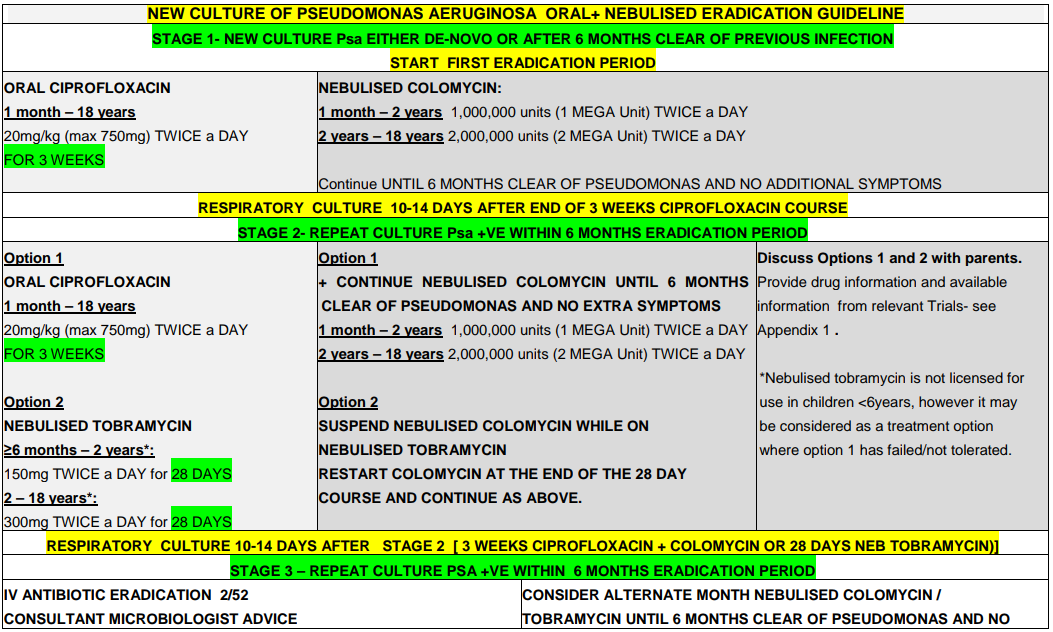
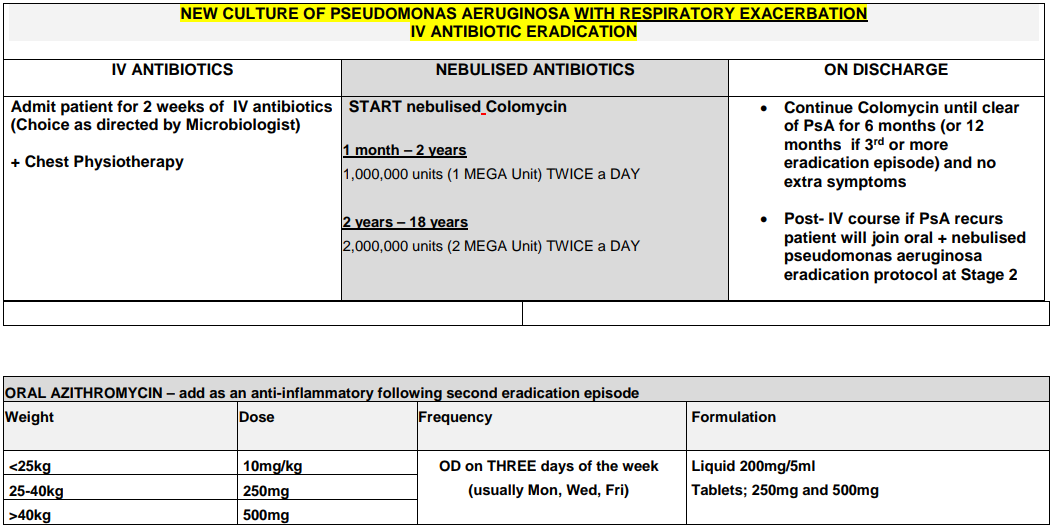
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is recognized as being a significant respiratory pathogen for patients who have Cystic Fibrosis (CF). Chronic colonisation with Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with poorer clinical outcome and attempted eradication on first culture is aimed at preventing this.1
Recommendation: When P. aeruginosa grows from respiratory culture for the first time (or where there is growth in a patient that has been clear of the organism for 6 months or more) eradication should be attempted.2
Please note: if Ps aeruginosa is resistant to Ciprofloxacin please seek Consultant Microbiologist advice.