Accurate measurement of the ventricles is important in both defining ventriculomegaly and also assessing progression. The fetal head should be scanned in the axial plane at the level of the frontal horns and the cavum septum pellucidum (CSP) (the same level at which a head circumference is taken), at an appropriate magnification that the head fills the screen. The callipers should be placed at the internal margins of the atrial walls at the level of the parietal occipital groove and the glomus of the choroid plexus, perpendicular to the axis of the ventricle.
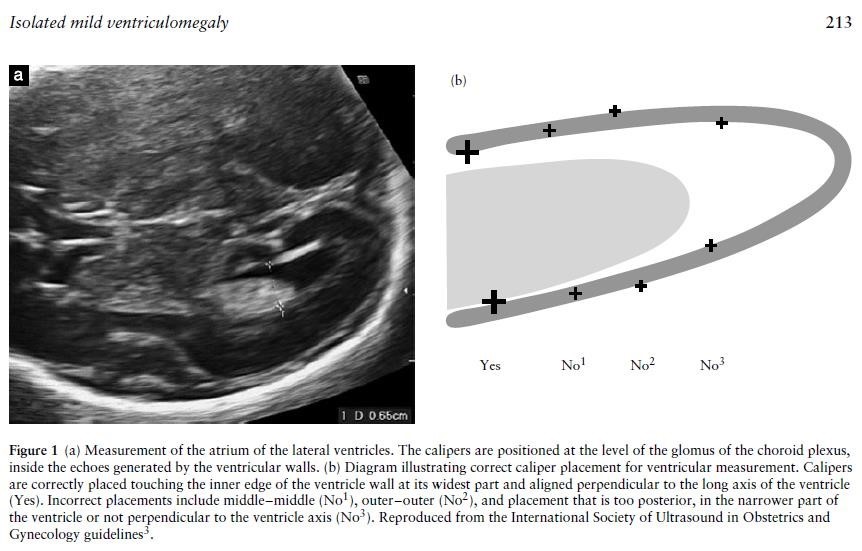
Although the distal ventricle is always easier to see than the proximal one because of reflection of the ultrasound beams from the fetal skull, both ventricles should be checked; ventriculomegaly is unilateral in 50-60% cases and bilateral in 40-50% (5).
