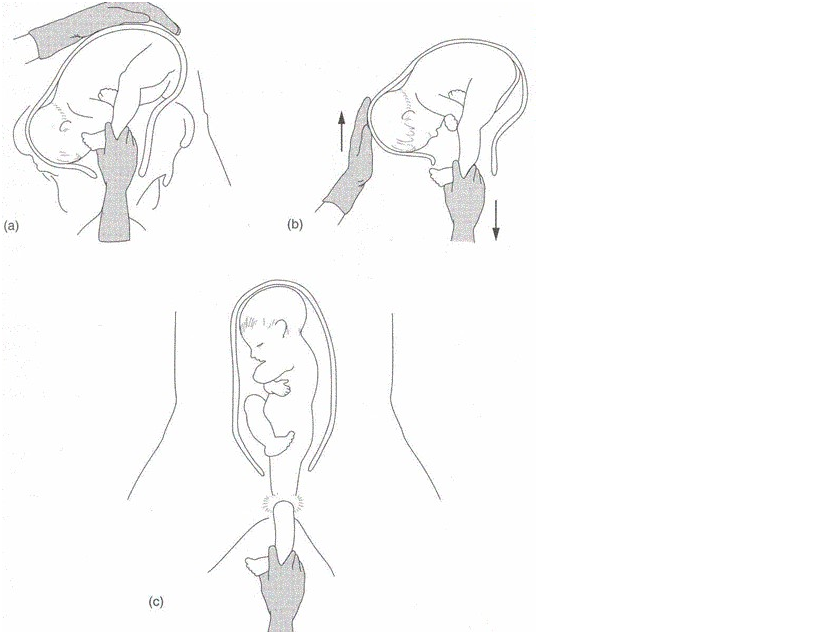
Fetal head entrapment during vaginal breech delivery is an obstetric emergency.
It is typically associated with preterm vaginal breech delivery when the fetal buttocks and trunk pass through an incompletely dilated cervix. The uterus subsequently contracts and clamps tightly around the fetal head.
N.B Entrapment can also occur at Caesarean section and although the reasons may be different the obstetrician needs to have a strategy (see Delivery of Breech at LUSCS)
Management of Entrapment at Vaginal Delivery
- Inform anaesthetist, paediatric staff, senior midwife
- Re-try Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit(MSV) manœuvre
- Rotate baby to sacrum transverse
- McRobert’s manoeuvre
- Suprapubic pressure
- Start tocolysis with GTN
1. Emergency cervico-uterine relaxation
Maternal IV cannula requires to be sited prior to administration of GTN (the drug may cause profound drop in BP)
Sublingual GTN via metered pump:
Nitrolingual pump spray should be primed before using it by pressing the nozzle once.
1 – 2 sprays (400-800 micrograms) administered as spray droplets beneath the tongue (do not inhale). Ask woman to close her mouth after spray is administered.
Repeat after 5 minutes if hypertonus is sustained.
Haemodynamic monitoring, a rapidly running I.V. infusion and immediately available ephedrine and phenylephidrine are mandatory prior to the use of Nitroglycerin (Glyceryl Trinitrate)
Cautions:
- Nitrates may increase intraocular pressure and so should be used with caution to glaucoma.
Contraindications:
- Uncorrected hypovolaemia
- Severe anaemia (Hb<60 g/L)
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Constrictive pericarditis /pericardial tamponade
- Hypersensitivity to GTN. Nitrates, coconut oil, ethanol, glycerol, monocarprylocaproate, peppermint oil
General Anaesthesia with a high end tidal concentration of volatile agent will often produce useful relaxation of the cervix
Once the third stage is complete, a Syntocinon infusion should be commenced.
2. Emergency surgical option: Cervical Incisions
Incise cervix - Duhrssen’s incisions @ 2,10 and 6 o’clock (see below)
 |
Pictorial diagram of Duhrssen's incision at 2,10 and 6 o’clock* |
*Incisions at 2 + 10 o’clock are usually sufficient. (PROMPT 2nd edition) Take great care to only cut the cervix
3. Emergency Surgical Option: Symphysiotomy Technique
- Lithotomy position for patient
- Analgesia
- Catheterise bladder (indwelling)
- Incise skin above the symphysis with a solid scalpel. The top of the symphysis is probed with the tip of the scalpel to identify the non-bony joint.
- The urethra is kept displaced from the midline by a finger in the vagina pushing the catheterised urethra laterally.
- The scalpel, held at an angle 30 degrees from the horizontal, is advanced vertically towards the vagina until the sharp tip is sensed by the intravaginal finger. Divide the joint by a sawing action.
- When the separation of the joint is felt remove the catheter, apply forceps and deliver the fetal head.
- An episiotomy and traction towards the sacral aspect of the pelvis relieves pressure on the unsupported urethra.
- After a symphysiotomy it is essential to refer to physiotherapy and orthopaedics for follow up as there can be significant morbidity.
4. Caesarean section after replacement similar to Zavanelli for Shoulder Dystocia (see shoulder dystocia guideline)