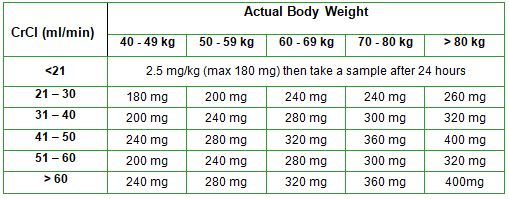
- Use the gentamicin calculator (also via intranet quicklinks) or use the table below to calculate an initial dose. (Calculate creatinine clearance (CrCl) using the Cockcroft–Gault equation below. Do not use eGFR).
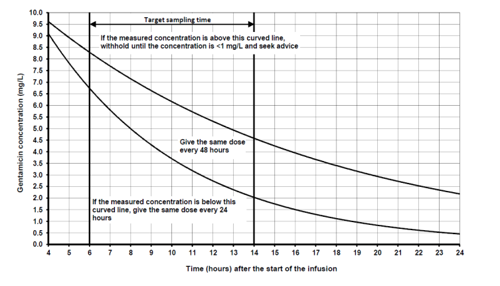
- Prescribe the first gentamicin dose on the "GENTAMICIN PRESCRIBING, ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING CHART". Also, prescribe gentamicin 'as per chart' on the regular section of the NHS Fife drug chart. Do not prescribe further doses until a level has been obtained.
- In patients with Acute Kidney Injury (≥50% increase in baseline serum creatinine or oliguria >6 hrs) give a single dose according to the table below and seek senior medical advice before giving a second dose.
- If the patient weighs less than 40kg and CrCl is >21ml/min, give a single dose of 5mg/kg, then monitor as below.
- If the creatinine is unknown give a single dose of 5mg/kg (maximum 400mg), then monitor as below.
- If known CKD 5, give 2.5mg/kg (maximum 180mg) on the advice of senior medical staff, then monitor as below.
- Obese patients or patients >90 years may require dose adjustments and require close monitoring. Contact Pharmacy for advice.
Table of initial gentamicin doses: