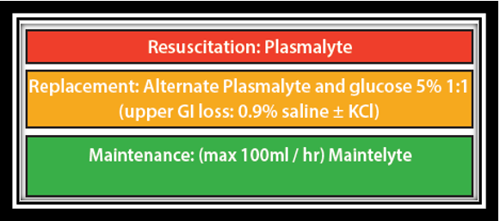
Fluids are prescribed for three generic scenarios:
- Resuscitation
- Replacement
- Maintenance
See: NICE Algorithms for IV fluid therapy in adults-poster-set-pdf-191627821. Page 1 copied below:

Resuscitation
- If your patient is haemodynamically unstable, follow the resuscitation guidelines in the NICE algorithm
- Make seniors aware urgently.
- Make note of fluid volumes used, if approaching 2L IV fluid, ensure referral has been made for HDU/ITU and consideration of inotropes if BP remains low.
Replacement
- A full set of bloods including levels of sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphate, calcium should be taken.
- You should also gain a VBG/ABG to assess blood glucose and pH to ensure you are not missing a DKA.
- This is not an exhaustive list of investigations; ensure you have taken an adequate history and examination and investigate as appropriate.
- First assess whether the patient can replace fluid and/or electrolytes orally.
- If able and safe levels to do so, oral replacement should be the preferred option (see NICE algorithm).
- If electrolytes are deranged, treat according to the following guidelines:
- Serum K < 3.5mmol/L: Hypokalaemia (Guidelines)
- Serum Na < 130mmol/L: Hyponatraemia (Guidelines)
- Serum Ca < 2.2mmol/L: Hypocalcaemia (Guidelines)
- Serum phosphate < 0.8mmol/L: Hypophosphataemia (Guidelines)
- Serum magnesium < 0.7mmol/L: Hypomagnesaemia (Guidelines)
- Hypernatraemia: discuss with senior clinician
- Hyperkalaemia: Hyperkalaemia: Secondary Care (Guidelines)
- Hypercalcaemia: Hypercalcaemia (Secondary Care) (Guidelines)
- In complex patients with multiple electrolyte disturbances, the above IV guidance will put them at high risk of fluid overload. In this scenario, discuss with senior clinician +/- registrar on call for SHDU or MHDU for consideration of CVC placement and concentrated electrolyte replacement.
- Please consider diluting electrolytes in 5% glucose in preference to 0.9% saline IF THIS IS A LISTED OPTION. This is to reduce use of 0.9% saline hospital-wide due to side effect of hyperchloraemic metabolic acidosis.
Maintenance
Maintenance fluids are required in patients who are clinically stable but cannot meet their basic daily intake needs due to poor swallow / reduced consciousness / background disease process. They are also required for patients who are temporarily NBM, eg, prior to surgery or intervention.
A full set of bloods, including sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphate and calcium levels should be taken.