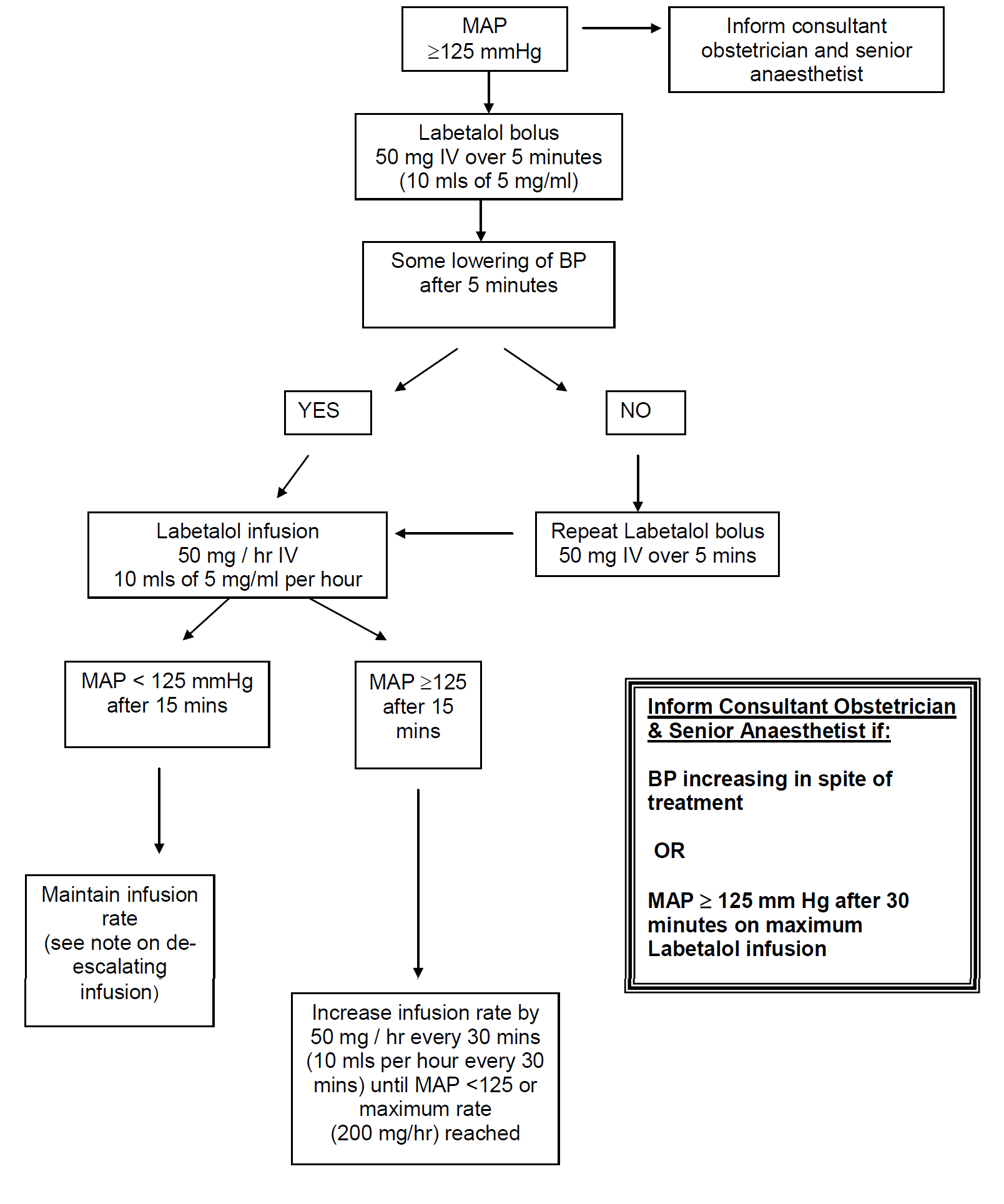
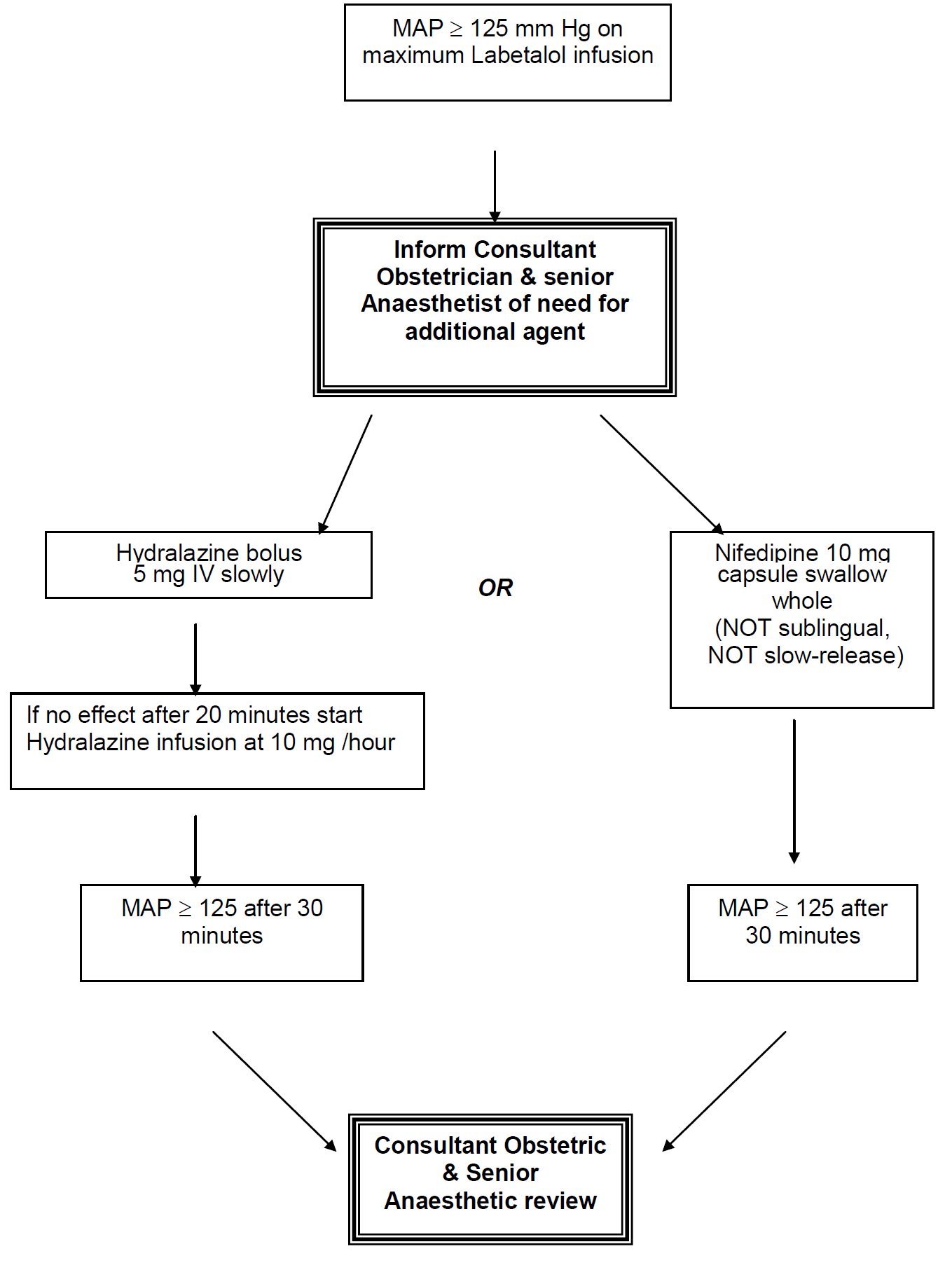
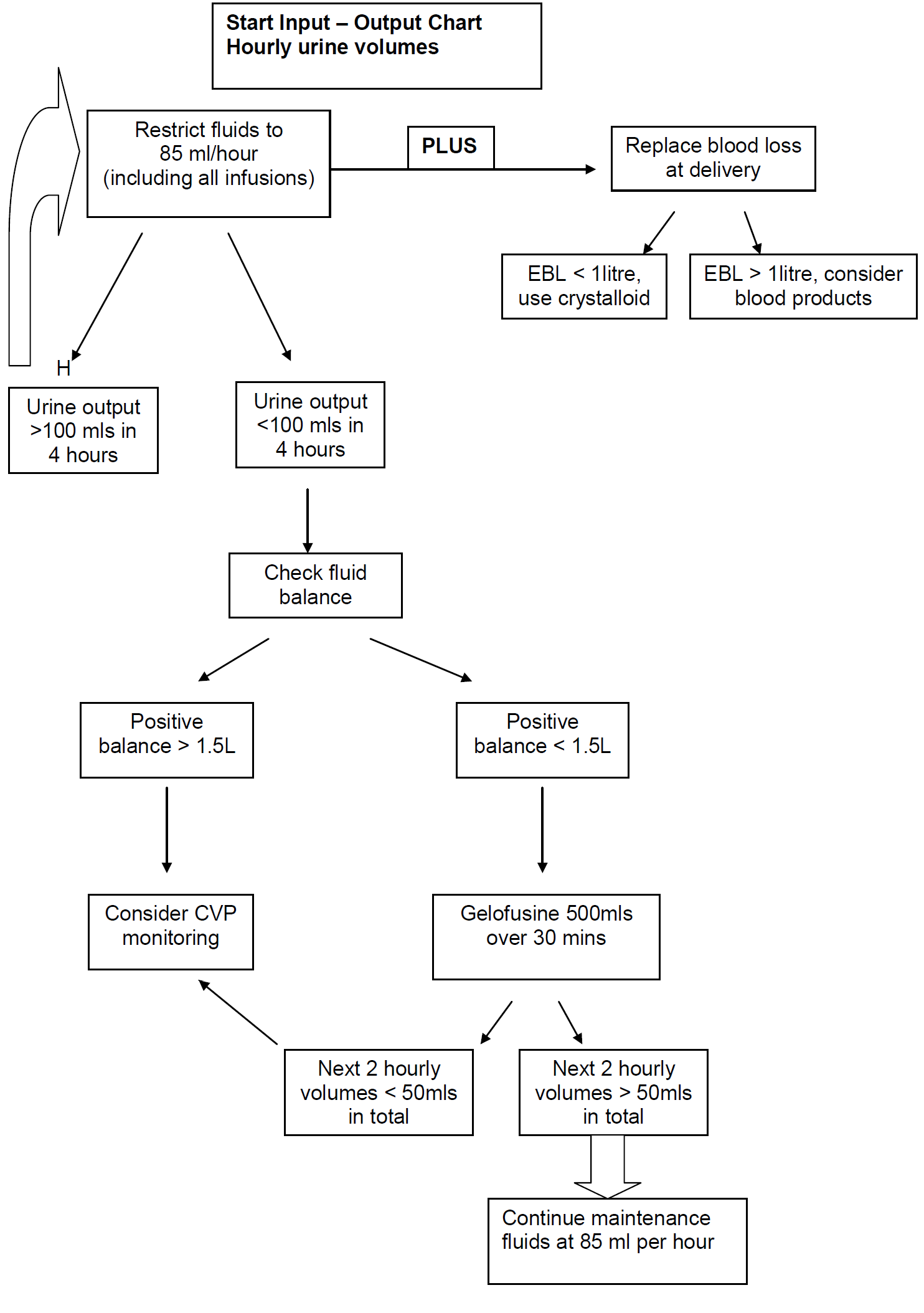
In severe preeclampsia consideration must be given to commencing seizure prophylaxis. This should be discussed with the consultant obstetrician when informing them of the patient presentation.
Magnesium Sulphate is the drug of choice unless there are specific contra indications to its use (pre-existing cardiac disease, acute renal failure, Myasthenia gravis).
Paediatricians should be informed if Magnesium Sulphate has been administered prior to delivery.
Magnesium Sulphate:
Loading Dose (by hand):
- 4 grams IV over 5 minutes
(Add 4 grams (8 mls of 50%) Magnesium Sulphate to 12 mls Normal Saline)
Maintenance Infusion Dose:
- IV infusion 1 gram Magnesium Sulphate per hour
Maintenance Infusion Preparation:
- 10 grams (20 mls of 50%) Magnesium Sulphate made up to 50 mls by adding to 30 mls normal saline in a 60 ml luer lock syringe
- Infusion rate is 1 gram (5 mls) per hour via an syringe driver
Infusion is maintained at 1 gram/hr for 24 hours provided:
- Respiratory rate > 14 per minute
- Urine output > 25mls/hour, and
- Patellar reflexes are present (use arm reflexes if regional anaesthesia)
NB: The volume of the Magnesium Sulphate infusion must be included as part of the total fluid maintenance infusion for the patient of 85ml/hour
Recurrent Seizures on Treatment:
- Give a 2nd bolus dose of Magnesium Sulphate 2 grams over 5 minutes by hand (do not stop infusion)
- add 2 grams (4 mls of 50%) Magnesium Sulphate to 6 mls of Normal Saline
- One dose only
If further seizures despite 2nd bolus give Diazepam 10mg IV. Intubation may be required to protect airway and ensure adequate oxygenation.
Magnesium Sulphate – Patient Monitoring:
Reflexes:
- Patellar reflexes after completion of loading dose and hourly whilst on maintenance dose (use arm reflexes if functional regional anaesthesia).
- If reflexes are absent stop infusion until reflexes return and check Magnesium level.
Oxygen Saturation / Respiratory Rate:
- Continuous O2 saturation should be assessed.
- Perform respiratory rate every 15 minutes
- If O2 saturation < 94% or respiratory rate < 14 / min, administer O2 (4 L/min via Hudson mask), stop Magnesium Sulphate infusion and call anaesthetist. Check Magnesium level. Consider antidote
Urine Output:
Monitor hourly.
If >20 ml/h - continue Magnesium Sulphate infusion.
If 10 - 20 ml/h & creatinine <150mmol/l - continue as protocol and recheck Magnesium level every 2 hours.
If 10 - 20 ml/h & creatinine > 150mmol/l (or urea >10) - recheck Magnesium levels immediately and every 2 hours. Decrease infusion rate to 0.5gram/hour.
If < 10 ml/h - stop infusion and check Magnesium level.
Biochemical Monitoring (Magnesium levels): This is not routine. If required then see below.
The Therapeutic range is 2-4 mmol/l.
Low If < 2 mmol/l - Maintain infusion at current rate. Recheck in 2 hours.
Therapeutic If 2 -3.5 mmol/l - Continue infusion at current rate. Recheck in 2 hours if clinical indication remains.
High If 3.55 - 5 mmol/l - STOP INFUSION for 15 min and then recommence at half previous infusion rate and recheck in 1 hour.
Very High If > 5mmol/l - STOP INFUSION and consider antidote. See below for further details.
Magnesium Sulphate toxicity and management:
|
Clinical Features
|
Mg level
|
Action
|
|
Loss of Patellar reflexes
Weakness
Nausea, Flushing
Double vision
Slurred speech
Somnolence
|
circa 5 mmol/l
|
STOP INFUSION
GIVE ANTIDOTE
10 ml of 10% Calcium Gluconate (1gram)
Slow IV inject over 10 mins.
CHECK Magnesium level.
|
|
Muscle Paralysis
|
circa 6-7.5 mmol/l
|
STOP INFUSION
GIVE ANTIDOTEAS ABOVECHECK
Magnesium level.
|
|
Respiratory Arrest
Cardiac Arrest
|
circa 12 mmol/l
|
STOP INFUSION
INSTITUTE CPR
2222 CALL Obstetric and cardiac arrest team INTUBATE AND VENTILATE
GIVE ANTIDOTE AS ABOVE
CHECK Magnesium level
|